National Deworming Day: FAQs On Intestinal Worms Or Soil-Transmitted Helminths (STH) Infections
World Health Organisation estimates that 241 million children (1-14 years old) in India are at risk of parasitic intestinal worms known ais Soil-Transmitted Helminths (STH). This means India accounts for approximately 28 per cent of the total number children globally estimated to be at-risk of STH infections. On National Deworming Day (February 10), here are answers to some frequently asked questions about intestinal worms or Soil-Transmitted Helminths (STH).
What Are Intestinal Worms?
Intestinal worms are parasites that live in the human intestines and consume nutrients and vitamins that is consumed. There are three main types of STH that infect people, roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides), whipworm (Trichuris trichiura) and hookworms (Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale). These worms depend on the human body for their food and survival and while being there, they lay thousands of eggs each day.
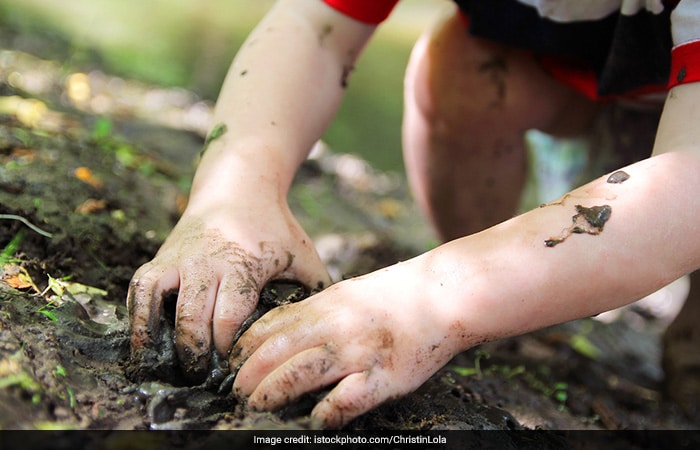

How Do People Get Infected With Worms?
Worm infections result from poor sanitation and hygiene conditions, and are transmitted from contact with infected soil, contaminated drinking water and food that is not carefully washed and prepared.
Infected people who defecate in the open spread worm eggs in their faeces. Subsequently, the eggs contaminate the soil which further adulterate food and water, spreading the infection.
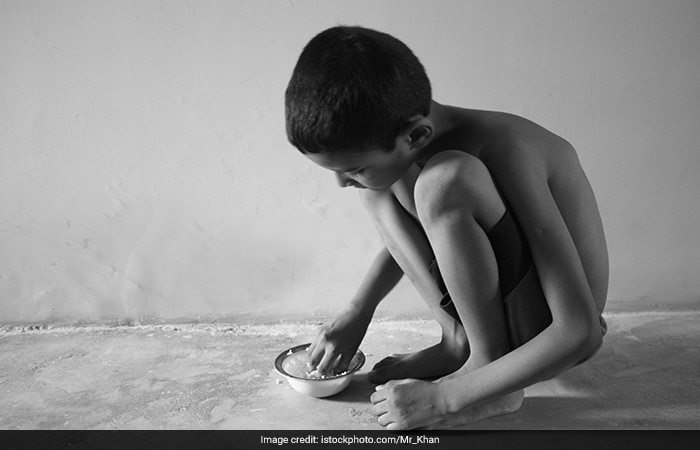

What Are The Harmful Impacts Of Worms Infestation?
Since worms feed on host (human body) tissues, including blood, it leads to loss of iron, and protein, resulting in anaemia - reduced oxygen carrying capacity due to less Haemoglobin (Hb) available in the body.
Worm infection can also lead to diarrhoea; dysentery; loss of appetite; reduced nutritional intake and physical fitness; increased malabsorption - a condition that prevents absorption of nutrients through the small intestine.

How To Treat Intestinal Worms?
The Government of India recommends the use of Albendazole, the deworming drug. Children between 2-19 years of age are recommended to take 1 tablet (400 mg) of Albendazole whereas children in the 1-2 years age group are advised to take half tablet of Albendazole. For young children the tablet should be broken and crushed and administered with water.
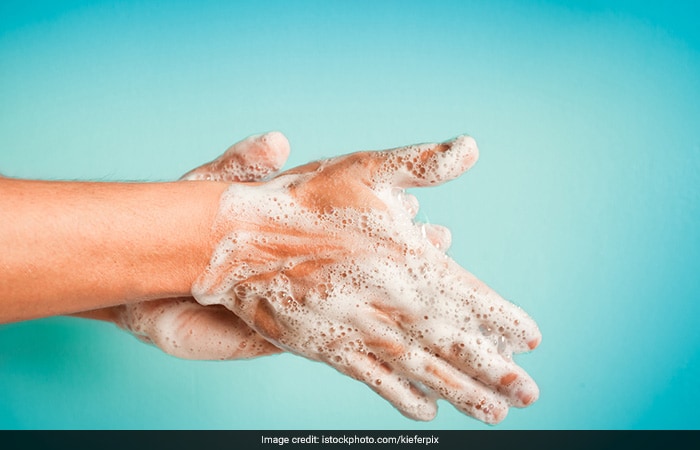

How To Prevent Worm Infestation?
Practise good hygiene and ensure clean surroundings. This includes, using sanitary toilets, not defecating in open; hand-washing especially before eating and after using toilets; wearing slippers and shoes; improving the quality of food consumed by optimal processing and cooking techniques.

















